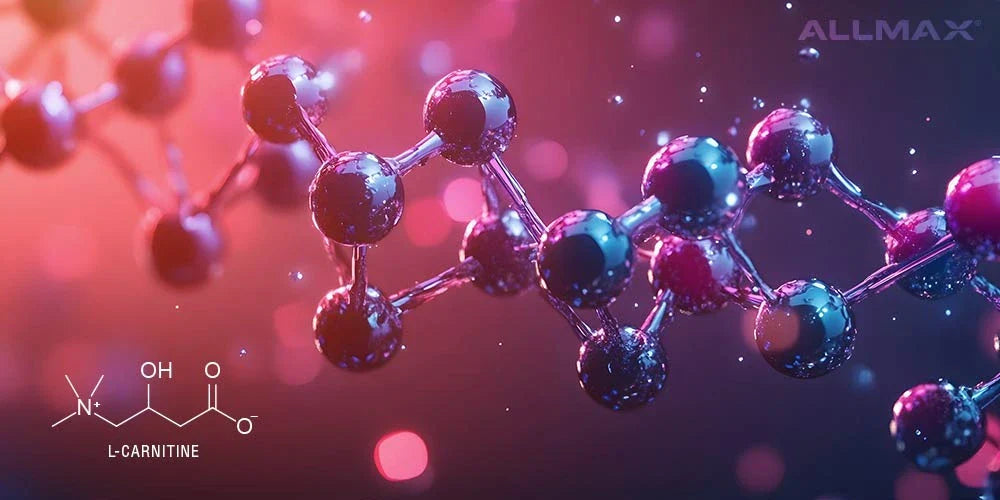
Milk thistle, also known as Silybum marianum, is a plant known for its medicinal properties. This herbal remedy has been used for centuries to support liver health and treat various conditions. In recent years, it has gained popularity as a natural supplement for overall well-being. But what exactly is milk thistle, and how can it benefit your health? Read on to learn about its potential benefits, side effects, and more.
What is Milk Thistle?
Milk thistle is a flowering plant native to the Mediterranean region. It’s best known for its distinctive purple flowers and spiky leaves with white veins. The plant's medicinal properties come primarily from its seeds, which contain silymarin. This compound is believed to protect liver cells, promote their regeneration, and combat oxidative stress.
Despite its long-standing reputation as a safe and effective supplement, research shows that not all commercial preparations deliver the expected therapeutic benefits. Some products may contain lower concentrations of silymarin due to poor-quality raw materials or even deliberate adulteration. Contaminants and foreign substances have also been found in certain milk thistle supplements, raising safety concerns.
What is Milk Thistle good for?
Milk thistle is primarily valued for liver health, but its benefits touch many aspects of wellness. Here’s a quick list of what this powerful herb may offer:
- Liver Support: Shields liver cells from toxins and supports tissue repair.
- Detoxification: Enhances the body's natural detox processes.
- Antioxidant Defense: Fights free radicals and reduces oxidative stress.
- Digestive Aid: Stimulates bile production for better digestion.
- Skin & Heart Health: May improve skin conditions and promote cardiovascular wellness.
To fully reap these benefits, it’s important to choose a high-quality supplement, like Cytogreens and Liver D-Tox . Packed with antioxidants and digestive enzymes, Cytogreens can help amplify your body’s detoxification process and boost overall vitality. By combining smart supplementation with a balanced lifestyle, you can give your body the comprehensive support it deserves!
Benefits of Milk Thistle
Milk thistle is most commonly associated with liver health, but its potential benefits extend beyond that. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Liver Support: Milk thistle is widely used as a complementary treatment for liver conditions, including cirrhosis, hepatitis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Silymarin helps shield liver cells from toxins and promotes the repair of damaged tissue.
- Detoxification: By supporting liver function, milk thistle aids the body’s natural detox processes, helping to eliminate harmful substances.
- Antioxidant Protection: Silymarin acts as a powerful antioxidant, reducing oxidative stress and combating free radicals that contribute to chronic diseases and aging.
- Digestive Health: Milk thistle can stimulate bile production, which improves digestion and helps break down fats.
- Skin Health: Some studies suggest milk thistle may help with skin conditions like acne and eczema due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Potential Anticancer Effects: Preliminary research indicates that silymarin may inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells, although more clinical studies are needed.
Side Effects of Milk Thistle
Although milk thistle is generally safe and well-tolerated when taken in appropriate doses, it can cause side effects in some people. These may include:
- Digestive Issues: Mild gastrointestinal symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, or nausea can occur, especially at higher doses.
- Allergic Reactions: People allergic to plants in the Asteraceae family (e.g., ragweed, daisies) may experience allergic reactions, such as rashes or itching.
- Drug Interactions: Milk thistle may interact with certain medications, particularly those processed by the liver, potentially altering their effects.
- Hormonal Effects: Due to its mild estrogenic activity, milk thistle might not be suitable for individuals with hormone-sensitive conditions, like breast or ovarian cancer.
References: